
Structures Around The Knee Joint:
Collaterals:
Medial Collateral Ligament:
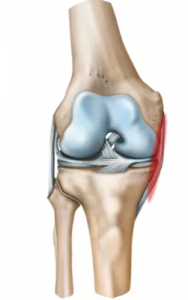
Also known as tibial Collateral ligament. Most common ligament to be injured is medial Collateral ligament. Because it is attached to the medial meniscus.
Lateral Collateral Ligament:
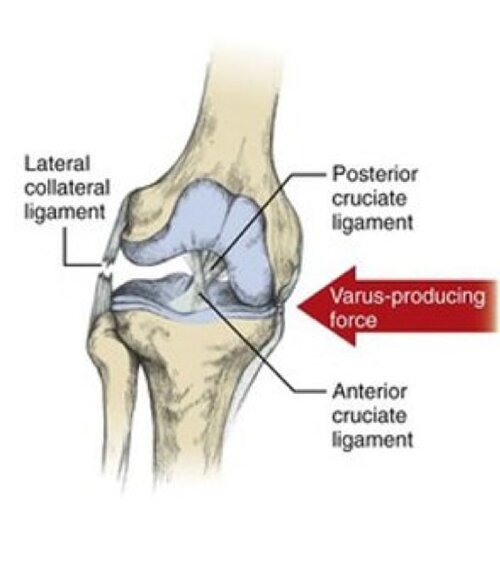
Also known as fibular Collateral ligament. poplitius tendon present inside the knee joint.
Meniscus and Cruciate ligaments are intracapsular. Lateral Collateral ligament and Medial Collateral ligament are extra capsular. these two ligament provide coronal plane stability and resist valgus force and varus force. Medial Collateral ligament is in tension in varus force. Lateral Collateral ligament is in tension in varus force.
Provocative test for medial Collateral ligament valgus stress test. Knee at 30 degree flexion.
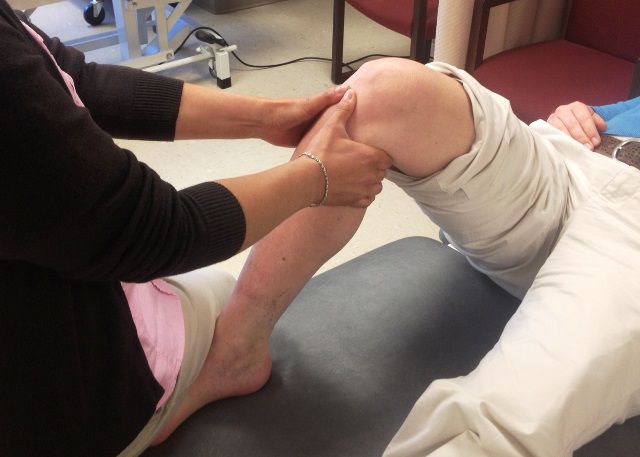
Provocative test for lateral Collateral ligament is varus stress test.
Investigation of choice for Collateral ligament injury is MRI.
Treatment: conservative (a brace should be applied). If improvement is not seen surgical intervention is required.
Meniscal Injury:
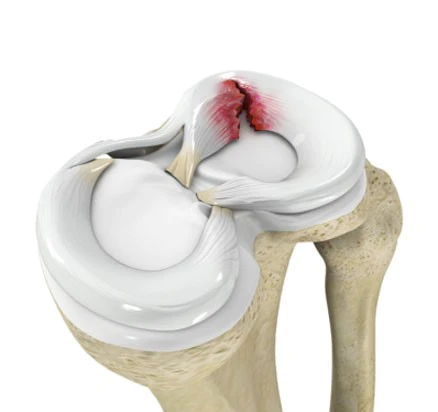
2 menisci- medial and lateral meniscus.
Collagen 1 is predominantly present in meniscus. Menisci are intracapsular and intrasynovial structures. Medial meniscal injury is more common than lateral meniscus because it is less stable. Medial meniscus adherent to medial Collateral ligament.
2 sources of Nutrition of meniscus: Peripheral area also called as Red zone blood. Central area also called as White zone Synovial fluid. Transition zone is also called as Red White zone. Tear in red zone can be repaired and Heals better due to abundant blood supply.
Tear in a white zone is treated by excision of the torn piece. Meniscus is also called as cushions of the knee joint. Forces causing meniscus injury are twisting force, rotational force, torsional force. Most common meniscal tear is seen in medial meniscus. Most common type of meniscal tear is Bucket handle tear which is vertical or longitudinal tear extending up to posterior horn and anterior horn. Reasons are less mobility, adherence to medial collateral ligament, the weight bearing axis of the knee.
Clinical Presentations of Meniscal Injury:
Fusion of knee or locking of knee it is due to injured piece of meniscus are between knee joint. Delayed effusion in seen in meniscal injury bulge sign or bulge test is seen in minimal fluid collection.
Provocative Test of Meniscal Injury:

- MC murray’s test.
- Apley’s grinding test.
- Thessaly test.
- Ege’s test.
Investigation of choice for meniscal injury is MRI.
Gold standard investigation for meniscal injury arthroscopy.
Cruciate Ligaments of Knee:
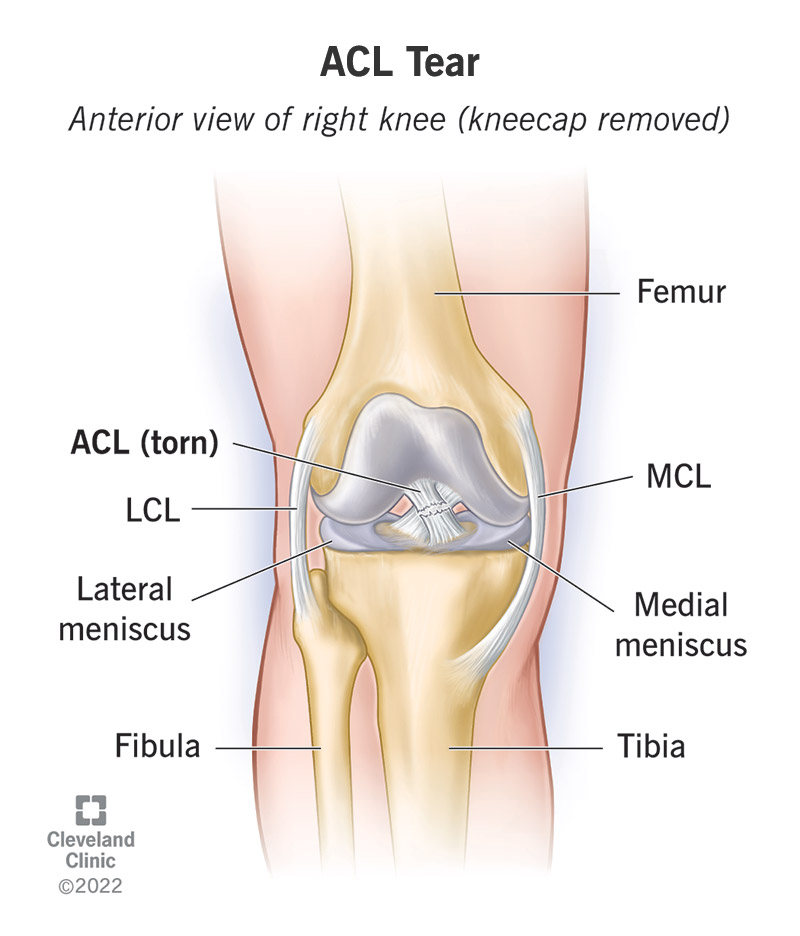
2 Cruciate ligaments are anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament. These ligaments provide sagittal Plains stabilization. These are intracapsular and extrasynovial in nature. Instability of knee is seen in anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament injury.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament:
Anterior cruciate ligament is most common to be injured. It prevent anterior translocation of tibia. It prevent hyper extension of knee. Ligament tear have difficulty in going up to the hill or stair. Usually tear in substance. In internal rotation anterior cruciate ligament is act as a primary rotational stabilizer.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament:
Posterior cruciate ligament is thicker and longer than anterior cruciate ligament. It prevent posterior translocation of Tibia. Posterior cruciate ligament is external rotation stabilization. Patient with posterior ligament tear have difficulty in going down hill or stair. It most commonly injure at bone. It is mostly injured in dashboard injury.
Mechanism of Twisting Injury to Knee:

When trauma occur to leg in fixed leg, flexed knee, valgus/lateral force/ abduction force , femur internally rotated. In that case injury to medial collateral ligament occur. Which result in injury to anterior collateral ligament and medial meniscus.
O’Donoghue Triad:
Medial collateral ligament, anterior collateral ligament and medial meniscus injury. It is also known as painful/ terrible/ unhappy triad of knee.
O’Donoghue test:
Test to assess cause of pain in the neck between cervical spine sprain vs cervical spine strain.
Investigation of Choice: MRI.
Treatment: reconstruction.
Arthroscopic anterior collateral ligament reconstruction:
Patient have rotational instability around knee joint.
Following tendon are used for graft: Hamstring, Semitendinosus, Gracilis, Patellar tendon.
Arthroscope / portals:

4mm/30 degree arthroscope used for knee. Angle of inclination of camera is 30 degree. Arthroscopy most commonly used for knee than shoulder. Anteromedial portals and anterolateral portals are 2 standard portals for knee.
Dial test:
Help us to identify injury to posterior lateral corner of knee.
Ankle Sprain:
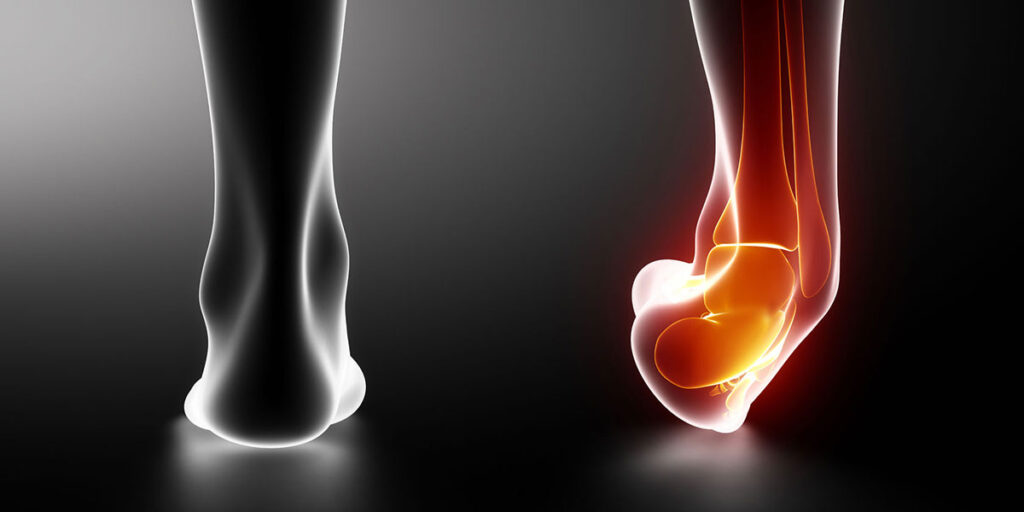
Most common method of ankle injury is inversion of plnatar-flexed foot in which lateral ligament stretched. Most common injured lateral ligament is anterior talofibular ligament. Most common injured ligament around knee medial collateral ligament. Most common mechanism of injury is inversion of foot. Most common injured tendon in body supraspinatus tendon.
Bulge sign:
Occurs in fusion of knee joint in medial meniscus injury. About 15-30 ml of fluid accumulated.
Insall-salvati ratio:
2 lengths are measured:
Length between tibial tuberosity and lower pole of patella – Length of patellar tendon(TL).
Length of patella(PL).
Patella alta: TL/PL more than 1.2.
Patella baja: TL/PL less than 0.8.
 Users Today : 8
Users Today : 8 Users Yesterday : 2
Users Yesterday : 2 Users Last 7 days : 20
Users Last 7 days : 20 Users Last 30 days : 71
Users Last 30 days : 71 Users This Month : 71
Users This Month : 71
This information very useful.please do more blog doctor.
🙏