
Chronic kidney disease- introduction:
CKD: decrease number of functioning nephrons
GFR: single nephrons GFR * number of functional nephrons
Interstitial fibrosis tubular atrophy glomerular sclerosis
TGF- beta: key molecule in pathogenesis of CKD
Chronic kidney disease- causes:
| Causes of CKD | Rate of fall of GFR |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 8-10 ml/min/year |
| Chronic glomerular nephropathy | 6-8 ml/min/year |
| Ischemic nephropathy | 4-6 ml/min/year |
| Chronic tubule-interstitial disease | 2-4 ml/min/year |
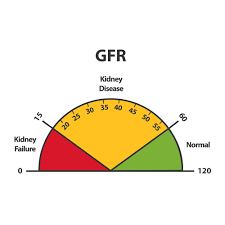
Grading of CKD:
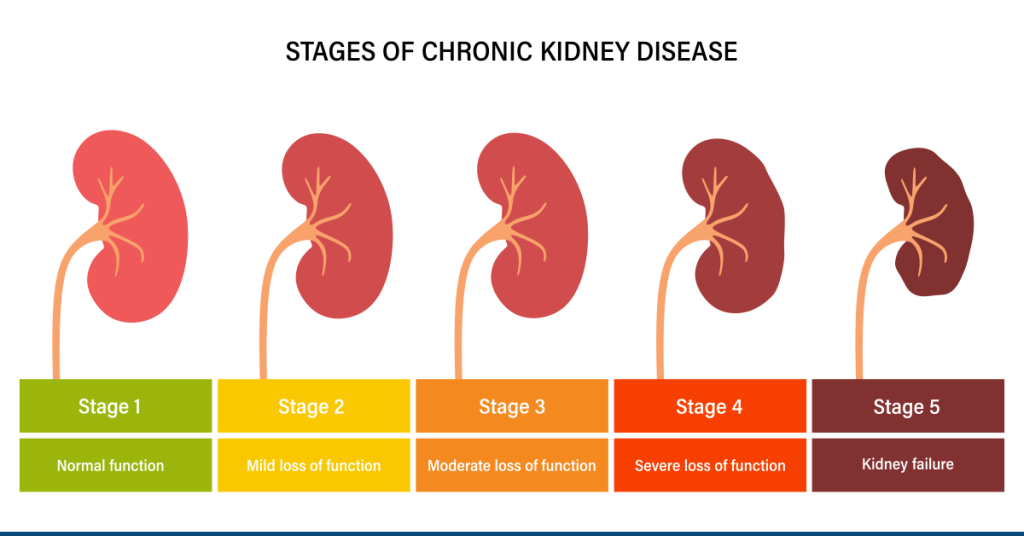
| Grades | GFR |
| Grade 5 | < 15 ml/min (End stage renal disease) |
| Grade 4 | 15 – 29 ml/min |
| Grade 3 | 30 – 59 ml/min |
| Grade 2 | 60 – 89 ml/min |
| Grade 1 | >90 ml/min |
Determinants of GFR:
Decrease nephron number causes increase intra glomerular pressure. Which result in increase in pore size of nephron. It gradually causes leakage of proteins.
Proteinuria – accumulation of proteins in podocyte ( angiotensin 2 mediated )
Decrease gene actctivation
TGF – beta
Chronic kidney disease – approach :
- A – Anemia , access , acidosis
- B – bone mineral disease , blood pressure
- C – cardiac
- D – dry weight , diuretic use
- E – electrolytes: Na , K , Ca , P
Uremia:
- Creatinine and urea : largely depend on GFR for excretion. An inverse relation with GFR.
- Phosphorus, uric acid, K ,H : tubules increase excretion as GFR declines. Either by excretion or decrease absorption.
- Na ( normal throughout CKD ): rate of excretion of Na per surviving nephron increase.
Access:
- AV fistula : least chance of infection. Take 6 weeks for maturation.
- AV graft
- Catheter : right IJV
- Temporary or cuffed tunnelled permanent catheter. Risk of infection.
Anemia in CKD:

< 12g/dl in male or < 11g/dl in female is anemia in CKD patient.
Target Hb to be achieved – 11g/dl
Anemia start appearing in CKD grade 3 onwards.
Anemia leads to progression of LVH, which result in to diastolic heart failure. Which finally results in to increase cardiovascular mortality. Anemia independently decrease GFR.
Causes for anemia in CKD:
- Absolute or relative deficiency of erythropoietin.
- Erythropoietin: produce from cortical and outer medullary peritubular interstitial fibroblasts.
- Anemia of chronic disease.
- Nutritional deficiency: iron deficiency anemia, folic acid , etc.
- Decrease red cell survival time in CKD.
- Increase PTH : bone marrow fibrosis.
- Uremia: bleeding
Investigations of anemia in CKD:
Pleuripotent hematopoetic stem cells – blood forming unit erythroid – colony forming unit erythroid – normoblast – reticulocyte – RBC
CKD patient with Hg 7.5 g/dl
Total leucocyte count − Normal
Platelets – Normal
- Hypo-proliferative
- Reticulocytes production index < 2
- Hyper-proliferative
- Reticulocyte production index > 2
- RPI= Hg of patient/ target Hg *reticulocytes/2
- MCV < 100 Fl
- Serum ferritin – iron store – decreased
- Serum ferritin – iron in circulation bound to transferrin – decrease
- TIBC – decrease
- % saturation of transferrin = decreased < 33%
Management of anemia in CKD:
Parenteral iron formulations:
- Iron sucrose 200mg
- Ferric carboxymaltose
- Ferric isomaltose
Erythropoietin therapy:
- Recombinant human EPO- EPO alpha: 1st generation
- 50 unit/kg/week
- Darbepoetin alpha : 2nd generation
- Methoxy polyethylene glycol beta
CKD – acidosis and blood pressure:
H + NH3 – NH4 : major form of acid excretion.
Up to grade 5 CKD : normal anion gap acidosis (NAGMA)
Grade 5 CKD : HAGMA + NAGMA
Issues with acidosis :
- Depression mayocardium
- Promotes calcification
- Diastolic disfunction
Blood pressure:
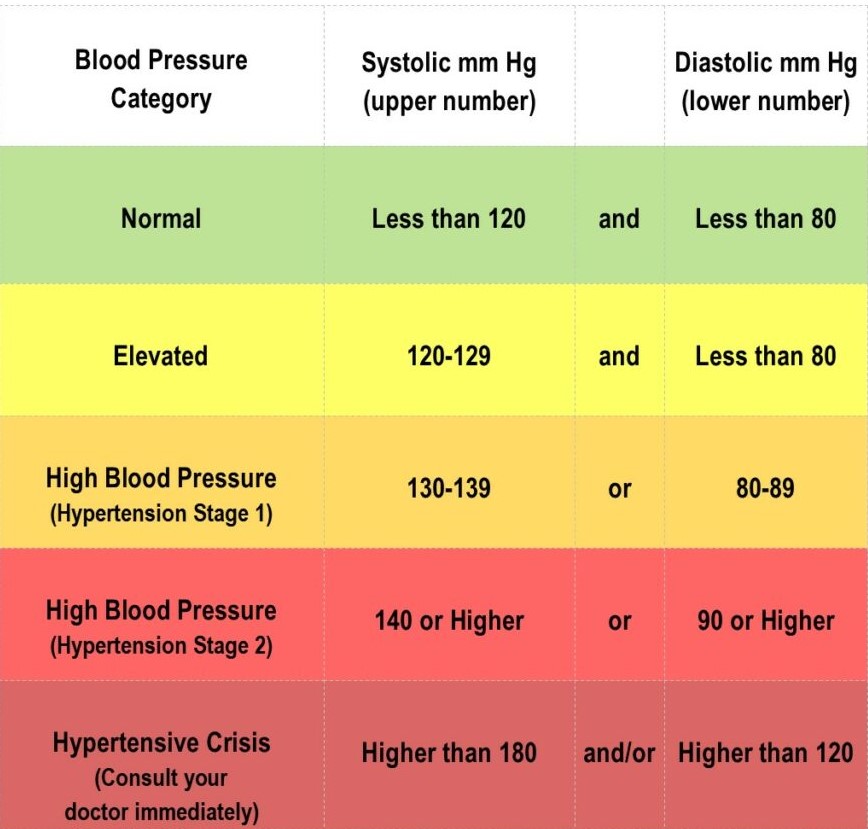
Blood pressure target in CKD : < 130/80
Preferred combination for treatment: ACE inhibitor or ARB + Ca channel blocker
24 hr ambulatory BP monitoring : preferred in CKD patients.
Bone mineral disease:
90% -high bone turnover – osteitis fibrosa cystica.
10% – low bone turnover – adynamic bone disease.
Phosphorus – normal endothelial cells – osteoblast – trap calcium.
Normal level of phosphorus : 2.5 -4.5 mg/dl.
>5.5 mg/dl
Osteocytes – FGF – 23 – inhibit reabsorption of phosphorus through klotho receptors. It causes resistance to phosphorus. It result in to hyperphosphatemia. Which ultimately present with calcification.
High bone turnover state :
- Decrease calcium
- Increase phosphorus
- Increase PTH – secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Increase bone formation
- Increase bone resorption
- No time for mineralisation
Ca(OH)2 Appatite – CaPO4
↓
Early fracture
Bone pain
Resorbed bone replaced by : bone + cyst + fibrous tissue
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
Low bone turnover state / adynamic bone disease : (PTH< 200pg/ml)
- Increase calcium supplements
- Drugs decrease PTH , increase calcium
- High Ca dialysate
Increase risk of calcification.
Management of high and low bone turnover state in CKD:
Treatment of high bone turnover:
Correction of hyperphosphatemia:
Pure phosphat binders: sevelamer , lanthanum, sucroferric oxyhydroxide
Calcium containing phosphate binders : in decreased calcium states : calcium acetate and CaCO3
Increase Ca , increase PTH : cincalcet – calcium sensing receptors agonist
Increase PTH
↲ ↳
Secondary hyperparathyroidism tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Decrease calcium PTH (>1500pg/ml)
Increase PTH increase calcium
Increase phosphorus increase phosphorus
Treatment of low bone turnover state : cutoff all calcium supplements
Cardiac manifestation in CKD:
ACS – most common death in CKD
Rate of rise of trop 1 : most preferred marker.
- LVH : diastolic dysfunction
- Calcification : irreversible
- Uremic toxins : asymmetric dimethyl arginine
- Malnutrition inflammation atherosclerosis
- Increased Oxidized LDL , increased small dense LDL
Sudden cardiac death : hyperkalemia
Cardiac evolution in CKD :
- Trop 1
- Standard ECHO
- Dobutamine stress test ECHO
- Angiogram
CKD – diuretic and electrolytes:
Diuretics:
Furosemide or torsemide
Diuretics resistance : tubular epithelial cells are clogged with uremic toxins
↓
Drug doesn’t enter lumen
Electrolytes:
K : causes sudden cardiac death
P : can convert vascular endothelial cells into osteoblast
↓
Calcification
Uremia:
uremic encephalopathy : 100% response to dialysis.
Uremic pruritus.
Uremic pericarditis – heparin free intensive dialysis .
Uremic gastritis.
 Users Today : 2
Users Today : 2 Users Yesterday : 3
Users Yesterday : 3 Users Last 7 days : 18
Users Last 7 days : 18 Users Last 30 days : 103
Users Last 30 days : 103 Users This Month : 74
Users This Month : 74